Booking Engine A Comprehensive Guide
Booking engines: They’re the unsung heroes of travel and countless other industries, silently orchestrating millions of reservations daily. From flights and hotels to rental cars and restaurant tables, these powerful systems streamline the booking process, connecting businesses with customers in a seamless and efficient manner. This guide dives into the heart of booking engine technology, exploring its functionality, key features, development considerations, and future trends. We’ll cover everything from choosing the right tech stack to optimizing for user experience and maximizing security.
We’ll explore different types of booking engines, examining their unique characteristics and the technologies that power them. We’ll also discuss crucial aspects like real-time updates, secure payment gateways, and the importance of a smooth, intuitive user experience across various devices. Get ready to unravel the complexities and appreciate the ingenuity behind this essential technology.
Defining a Booking Engine
Source: behance.net
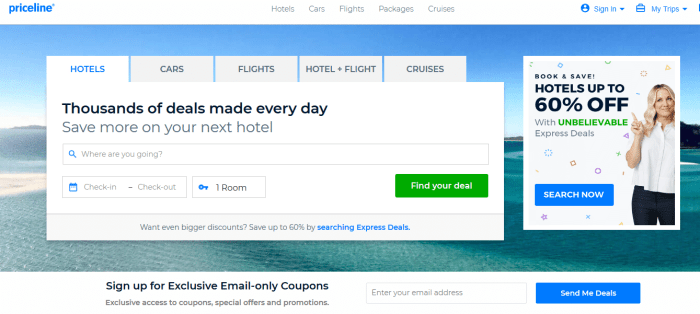
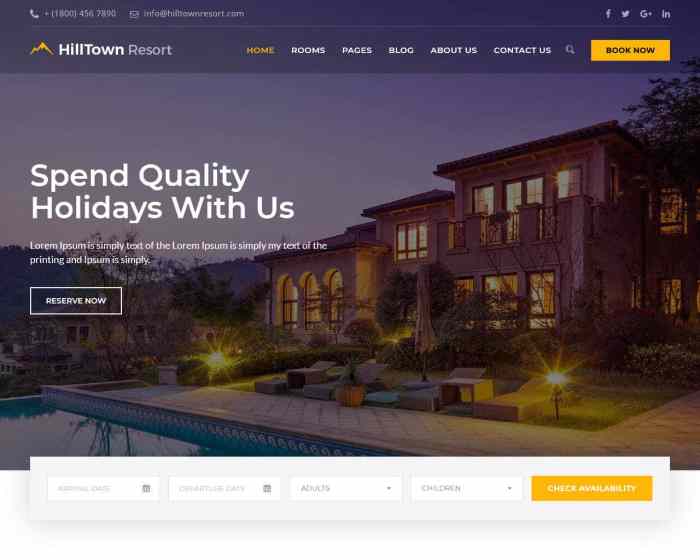
A booking engine is a software system that allows users to search for, select, and reserve various services online. It’s the backbone of many online travel agencies and directly supports businesses offering services that require reservations. Think of it as a highly automated, user-friendly version of a traditional reservation system.
Booking engines streamline the process of making reservations, eliminating the need for phone calls or emails. They automate tasks such as availability checks, payment processing, and confirmation delivery, offering a seamless experience for both the user and the service provider. This efficiency translates to increased bookings and reduced administrative overhead.
Types of Booking Engines
Different types of booking engines cater to specific industries and service offerings. The core functionality remains similar—search, selection, and reservation—but the specifics of what is being booked vary greatly.
- Hotel Booking Engines: These engines allow users to search for hotels based on location, dates, price range, amenities, and other criteria. They display available rooms, prices, and photos, and facilitate the booking process, often integrating with payment gateways and hotel management systems. Examples include those used by Expedia, Booking.com, and individual hotel chains.
- Flight Booking Engines: These engines focus on air travel, allowing users to search for flights based on origin, destination, dates, and number of passengers. They display flight options from various airlines, including prices, flight durations, and layover information. Successful implementations are found on sites like Kayak, Google Flights, and Skyscanner.
- Rental Car Booking Engines: These engines specialize in car rentals, allowing users to search for vehicles based on location, dates, vehicle type, and other preferences. They display available cars, prices, and terms and conditions, facilitating the reservation and often integrating with insurance providers. Examples include Enterprise’s website and those of other major rental car companies.
Examples of Successful Booking Engine Implementations
Several companies have successfully implemented booking engines, demonstrating their effectiveness in driving bookings and improving customer experience. Booking.com, for example, is a massive online travel agency that uses a sophisticated hotel booking engine to connect millions of travelers with hotels worldwide. Its success is attributed to its user-friendly interface, extensive inventory, and competitive pricing. Similarly, Expedia’s comprehensive platform integrates flight, hotel, and rental car booking engines, providing a one-stop shop for travel planning. Airbnb’s engine focuses on unique accommodations, demonstrating the adaptability of this technology to various market segments.
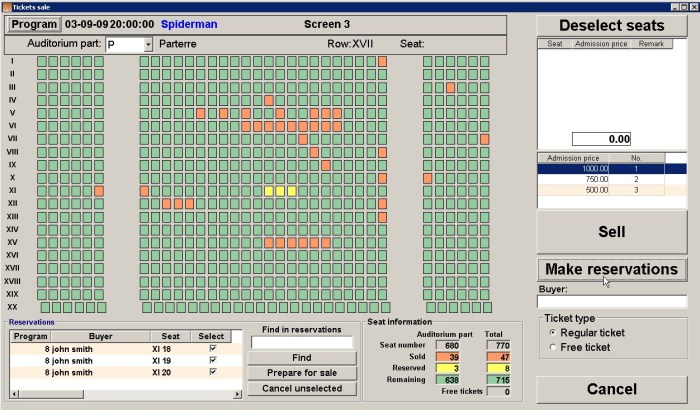
Booking Process Flowchart
A typical booking engine follows a straightforward process. Imagine a visual representation, a flowchart, starting with a user search. The user inputs their search criteria (e.g., destination, dates, number of guests for a hotel booking). The engine then queries its database to retrieve relevant results, displaying available options. The user selects their preferred option and proceeds to input their personal details and payment information. The engine processes the payment, confirms the booking, and sends a confirmation email to the user and notification to the service provider. The entire process is designed to be seamless and efficient, minimizing friction and maximizing conversion rates.
Key Features of a Booking Engine

Source: five.co
A successful booking engine needs more than just a pretty interface; it requires a blend of functionality and user-friendliness to drive conversions. Think of it as your digital storefront – it needs to be easy to navigate, secure, and offer a seamless booking experience. This section details the essential features to include.
Real-Time Availability and Pricing
Real-time updates are crucial for a smooth booking process. Imagine trying to book a flight only to find out the flight is already full after selecting your dates and seats. Frustrating, right? A booking engine with real-time availability ensures that users see accurate information, preventing double-bookings and disappointed customers. Similarly, real-time pricing prevents confusion and ensures transparency. Dynamic pricing models, where prices adjust based on demand and other factors, are common and require a robust system to handle these updates instantly. This dynamic pricing feature is often integrated with inventory management systems to provide a holistic view of availability and pricing.
Secure Payment Gateways
Security is paramount. Customers need to trust that their financial information is safe. Integrating secure payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, or Authorize.Net is essential. These gateways handle sensitive data according to industry best practices (like PCI DSS compliance), protecting both your business and your customers. Displaying security badges and clearly stating your commitment to data protection builds confidence and encourages bookings.
Customer Support Integration
Providing excellent customer support is key to building trust and resolving issues quickly. Integrating a live chat feature allows for immediate assistance, addressing queries and resolving problems in real-time. A comprehensive FAQ section can handle common questions, reducing the burden on your support team. Email support should also be available for less urgent inquiries. Think of it as having a helpful sales associate always available to assist customers throughout their booking journey.
Essential Features Table
A well-designed booking engine should include several key features to provide a positive user experience. Below is a comparison of three hypothetical booking engines, highlighting their feature sets:
| Feature | Engine A | Engine B | Engine C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time Availability | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Secure Payment Gateway | Stripe, PayPal | PayPal | Stripe, Authorize.Net |
| Customer Support (Live Chat) | Yes | No | Yes |
| Multiple Language Support | No | Yes | Yes |
| Mobile Responsiveness | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Booking Calendar | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Detailed Booking Confirmation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Email Reminders | Yes | No | Yes |
Technology Stack for a Booking Engine
Source: fiposoft.com
Building a robust and scalable booking engine requires careful consideration of the underlying technology. The right stack will directly impact performance, security, and maintainability. Choosing the appropriate technologies depends on factors like budget, project scale, and specific features required.
Programming Languages and Frameworks
The choice of programming languages and frameworks significantly influences the development process and the final product’s performance. Popular options often include backend languages like Python (with frameworks such as Django or Flask), Node.js (with Express.js), Ruby on Rails, or Java (with Spring Boot). These languages offer robust features for handling complex booking logic, database interactions, and API integrations. For the frontend, JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js are frequently used to create dynamic and user-friendly interfaces. The selection often depends on developer expertise and project requirements. For example, Python’s Django framework offers a structured approach, suitable for larger, more complex projects, while Node.js with Express.js provides a flexible and scalable solution ideal for microservices architecture.
Database Technologies
A reliable database is crucial for storing and managing booking data efficiently. Relational databases like PostgreSQL or MySQL are commonly used due to their ability to handle structured data and support complex queries. NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB or Cassandra, are also viable options, particularly when dealing with large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data, like user reviews or geographical location data. The choice depends on the anticipated data volume and the complexity of data relationships. For instance, a large hotel chain might benefit from a scalable NoSQL database to handle millions of booking records and associated user information efficiently.
API Integrations
Seamless integration with external services is vital for a comprehensive booking experience. Payment gateway APIs (e.g., Stripe, PayPal) are essential for secure online transactions. Mapping APIs (e.g., Google Maps) enhance user experience by providing location information and route planning. Calendar APIs (e.g., Google Calendar) enable users to easily synchronize their bookings. Review platforms APIs (e.g., TripAdvisor) can help gather customer feedback. These integrations streamline the booking process and provide a richer user experience. For example, integrating a payment gateway API ensures secure and efficient processing of payments, while a mapping API provides users with visual representations of locations and simplifies the process of finding the booked item.
Technology Challenges in Building a Scalable Booking Engine
Building a scalable booking engine presents several technological challenges. Handling high traffic loads during peak seasons requires robust infrastructure and efficient load balancing. Ensuring data consistency and availability across multiple servers is crucial for maintaining a reliable service. Security is paramount, requiring protection against various threats, including data breaches and denial-of-service attacks. Real-time availability of inventory information and accurate pricing are essential to prevent overbooking. Finally, effective monitoring and logging are vital for identifying and resolving performance issues promptly. For instance, a sudden surge in bookings during a holiday weekend could overwhelm a poorly scaled system, leading to service disruptions. Therefore, robust load balancing and infrastructure are essential to handle such peaks.
User Experience (UX) in Booking Engines
Source: beheerpaneel.nl
A seamless and enjoyable booking experience is crucial for the success of any booking engine. Poor UX can lead to abandoned bookings, negative reviews, and ultimately, lost revenue. Therefore, understanding and implementing effective UX strategies is paramount. This section will explore key aspects of UX design within the context of a restaurant reservation booking engine.
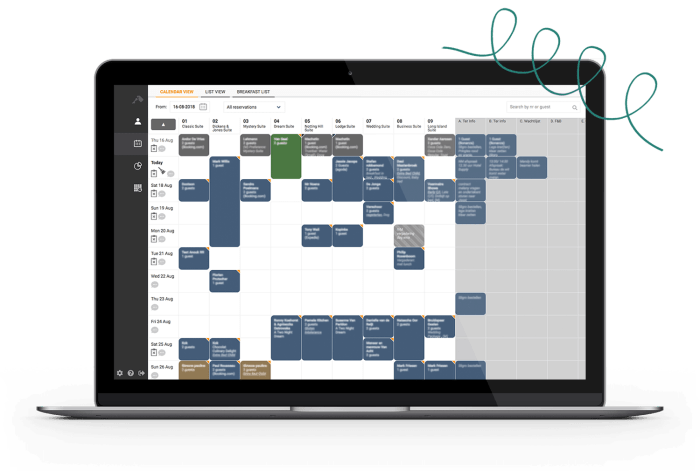
Restaurant Reservation Booking Engine UI Mockup
Imagine a clean, modern interface. The top features a prominent search bar allowing users to input the restaurant name, location, or date. Below this, a calendar widget displays available dates, highlighted in a visually appealing way. Once a date is selected, a time selection menu appears, showing available reservation slots in clear intervals (e.g., 6:00 PM, 6:30 PM, 7:00 PM). A section clearly displays the restaurant’s name, address, and a thumbnail image. A form then appears, requesting the number of guests, the customer’s name, email address, and phone number. A confirmation button, styled with a clear call to action (e.g., “Book Now”), concludes the process. Error messages are displayed concisely and helpfully should any input be invalid. The overall color scheme is calming and sophisticated, using a palette that reflects the restaurant industry. Typography is clear and easy to read.
Strategies for Optimizing the Booking Process
Minimizing friction in the booking process is achieved through a combination of techniques. Firstly, the form should be short and concise, requesting only essential information. Secondly, clear and immediate feedback should be provided after each step. For example, a progress bar could visually indicate the user’s progress. Thirdly, the use of autocomplete features for fields like address and email can save time and effort. Finally, the entire process should be designed to be quick and intuitive, encouraging completion rather than abandonment. A clear and visible progress indicator helps users understand where they are in the process and how much further they need to go.
Examples of Intuitive Design Elements
Many successful booking engines employ intuitive design elements. OpenTable, for instance, utilizes a clear calendar view for date selection, making it easy to identify available times. They also incorporate high-quality restaurant images and descriptions, enhancing the user experience. Booking.com uses filters and sorting options to help users narrow down their choices, making the search process more efficient. These examples demonstrate the power of intuitive design in facilitating easy and efficient bookings.
Mobile Responsiveness in Booking Engines
Mobile responsiveness is no longer optional; it’s essential. A significant portion of online bookings originate from mobile devices. A non-responsive design leads to a frustrating user experience, potentially resulting in lost bookings. The booking engine must adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and orientations, maintaining its functionality and usability across all platforms. This requires careful consideration of layout, font sizes, and interactive elements. A well-designed mobile-responsive booking engine ensures that users can easily make reservations regardless of their device.
Booking Engine Security
Source: dribbble.com
Building a secure booking engine is paramount; a breach can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Protecting user data and ensuring the smooth, trustworthy operation of your platform is essential for success. This section details critical security considerations for your booking engine.
Protecting user data and financial information requires a multi-layered approach. Neglecting security can result in severe consequences, including hefty fines and a loss of customer trust. A robust security strategy must be built into the system from the ground up.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities
Booking engines, by their nature, handle sensitive information like credit card details, personal addresses, and travel itineraries. This makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Common vulnerabilities include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure storage of sensitive data. Furthermore, unpatched software and weak password policies can significantly weaken security. For example, a poorly coded payment gateway could expose sensitive financial information during transactions. Another vulnerability is the lack of robust input validation, which allows malicious code to be injected into the system.
Best Practices for Data Protection
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for maintaining user trust and complying with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA. These best practices include using strong encryption for all sensitive data both in transit (HTTPS) and at rest (database encryption), implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts, and regularly updating all software and plugins to patch known vulnerabilities. Employing a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to filter malicious traffic and using secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities are also essential. Regular security testing is vital to identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited. For instance, storing credit card details using Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliant methods is mandatory.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing are not optional; they are critical for proactively identifying and mitigating security risks. A security audit provides a comprehensive assessment of your system’s security posture, identifying weaknesses in your security controls. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to uncover vulnerabilities that might be missed during an audit. Think of these as regular health check-ups for your booking engine. Scheduling these at least annually, and more frequently for high-traffic sites, is a prudent investment. For example, a penetration test might reveal a vulnerability in your authentication system that could allow unauthorized access to user accounts.
Implementing Robust Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms
Strong authentication and authorization mechanisms are fundamental to a secure booking engine. This means using secure password policies (requiring complexity, length, and regular changes), implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security, and employing role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles. For example, a booking agent should only have access to booking information, not financial data. Authorization should be carefully managed to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive areas of the system. Implementing these features greatly reduces the likelihood of successful attacks and minimizes potential damage.
Marketing and Optimization of a Booking Engine

Source: behance.net
A successful booking engine isn’t just about functionality; it needs a robust marketing strategy to attract customers and drive bookings. Integrating your booking engine seamlessly with your overall website marketing is key to maximizing its potential. This involves promoting the engine effectively, tracking its performance, and continuously optimizing for higher conversion rates.
Effective marketing ensures your booking engine isn’t just a feature, but a revenue-generating asset. By understanding how users interact with the engine and analyzing key performance indicators, you can refine your approach and increase profitability. This section explores various strategies and techniques to achieve this.
Integrating the Booking Engine with Website Marketing
Successful integration means the booking engine feels like a natural extension of your website, not an afterthought. This involves consistent branding, clear calls to action, and a user-friendly design that aligns with your overall website aesthetic. For example, if your website emphasizes high-quality photography, your booking engine should reflect that same visual style. Similarly, the language used should match the tone and voice of your website copy. Strategic placement of the booking engine – prominently featured on key pages like the homepage and service pages – is also crucial for visibility. A well-integrated booking engine increases user convenience and minimizes friction in the booking process, leading to higher conversion rates.
Effective Marketing Techniques to Increase Bookings
Several marketing techniques can significantly boost booking engine performance. Search Engine Optimization () is crucial to ensure your website and booking engine appear in relevant search results. This includes optimizing website content, meta descriptions, and image alt text with relevant s related to your services. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising on platforms like Google Ads can drive targeted traffic directly to your booking engine. Social media marketing, utilizing platforms like Instagram and Facebook, can showcase your services visually and engage potential customers. Email marketing can nurture leads and remind potential customers about upcoming bookings or special offers. Finally, leveraging partnerships with complementary businesses can expand your reach and attract new customers.
Using Analytics to Track Performance and Optimize Conversion Rates, Booking engine
Data-driven optimization is essential for maximizing booking engine performance. Tools like Google Analytics provide valuable insights into user behavior, identifying areas for improvement. Key metrics to track include bounce rate (percentage of visitors who leave the website without interacting further), conversion rate (percentage of visitors who complete a booking), average booking value, and time spent on the booking page. Analyzing these metrics helps pinpoint bottlenecks in the booking process and areas needing design or functional improvements. For instance, a high bounce rate on the booking page might indicate a confusing interface or slow loading times, prompting a redesign or technical optimization.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for a Booking Engine
A set of carefully selected KPIs provides a clear picture of your booking engine’s success. These include:
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of website visitors who complete a booking.
- Average Booking Value (ABV): The average revenue generated per booking.
- Booking Volume: The total number of bookings made within a specific time period.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer through marketing efforts.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The profitability of your booking engine marketing investments.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave the booking page without completing a booking.
- Average Session Duration: The average time spent on the booking page.
Regular monitoring of these KPIs allows for data-driven decision-making, enabling you to refine your marketing strategies and optimize the booking engine for maximum effectiveness. For example, a low conversion rate might signal the need for improved website design or a more streamlined booking process. High CAC could indicate inefficient marketing spend, necessitating a review of advertising strategies.
Future Trends in Booking Engines
Source: dribbble.com
The travel and hospitality industries are constantly evolving, and booking engines must adapt to stay competitive. Future trends are driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer expectations, leading to a more personalized, efficient, and seamless booking experience. We’ll explore some key areas shaping the future of booking engines.
Artificial Intelligence in Booking Engines
AI is revolutionizing booking engines, offering significant improvements in efficiency and personalization. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict user preferences, optimize pricing strategies, and personalize the entire booking journey. For example, AI can suggest optimal travel dates based on historical data and current demand, or recommend specific hotels or flights based on a user’s past booking history and stated preferences. This goes beyond simple filters; AI anticipates needs and proactively suggests relevant options. Moreover, AI can automate tasks like customer service inquiries, reducing response times and improving overall customer satisfaction.
Personalized Recommendations and Dynamic Pricing
Personalized recommendations are no longer a luxury but a necessity in a competitive market. By leveraging AI and machine learning, booking engines can deliver highly targeted recommendations based on individual user profiles, past behavior, and real-time data. This includes suggesting specific accommodations, activities, or transportation options tailored to a user’s interests and budget. Dynamic pricing, another AI-driven feature, optimizes pricing in real-time based on factors such as demand, seasonality, and competitor pricing. This ensures that booking engines offer competitive prices while maximizing revenue. Consider a flight booking engine adjusting prices based on the number of seats remaining and the time until departure—a classic example of dynamic pricing in action.
Voice Assistants and Chatbot Integration
Voice assistants and chatbots are transforming how users interact with booking engines. Integrating these technologies allows users to book travel arrangements through voice commands or natural language conversations. This hands-free approach enhances convenience and accessibility, particularly for users on the go. Chatbots can also provide instant support, answer frequently asked questions, and guide users through the booking process, leading to a more efficient and satisfying experience. Imagine booking a hotel room simply by asking your smart speaker, or instantly getting answers to questions about baggage allowance through a chatbot on the booking engine website—these are examples of how this integration streamlines the process.
Innovative Features Enhancing User Experience
Several innovative features are emerging to further enhance the user experience in booking engines. Augmented reality (AR) could allow users to virtually tour hotels or destinations before booking, providing a more immersive experience. Virtual reality (VR) could offer similar benefits, allowing users to explore destinations from the comfort of their homes. Integration with loyalty programs and reward systems can further incentivize users to book through the engine, fostering brand loyalty. Furthermore, the incorporation of advanced search filters and interactive maps enhances the user’s ability to find the perfect travel options based on specific needs and preferences. For instance, a filter that allows users to specify the type of view from their hotel room (ocean view, mountain view, etc.) or a map that clearly displays transportation links from the accommodation to major attractions would greatly enhance the search experience.
Final Wrap-Up

Source: therevolutorsonline.com
Building a successful booking engine requires a careful balance of technical expertise, user-centric design, and a keen understanding of market trends. From the initial conceptualization to ongoing optimization, every stage demands meticulous attention to detail. By understanding the core functionalities, key features, and potential challenges involved, developers and businesses can leverage the power of booking engines to streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive revenue growth. The future of booking engines is bright, promising even more personalized, intuitive, and efficient experiences fueled by AI and innovative technologies. This guide has provided a solid foundation; now it’s time to build your own successful booking engine.